Heat Flux Sensors: How They Work and What They’re Used For
Introduction
Heat is an essential aspect of our daily lives, from cooking our food to heating our homes. Understanding the flow of heat is crucial for various industries, including HVAC, automotive, and aerospace, among others. Heat flux sensors play a critical role in measuring heat flow and temperature distribution, providing valuable information for temperature control and process optimization. In this article, we will delve into the science behind heat flux sensors, how they work, and what they’re used for.
What is a Heat Flux Sensor?
A Heat Flux Sensor, also known as a heat flow meter, is a device used to measure the flow of heat energy through a material. Heat flux sensors measure energy flux onto or through a surface in [W/m²].
The Hukseflux FHF05 Heat Flux Sensor is a specific type of heat flux sensor that is used in various applications such as building energy management, HVAC systems, and fire research.
The Hukseflux FHF05 is a thin and compact device that is placed on the surface of the material being studied. It measures the amount of heat being transferred through the material and converts it into an electrical signal. The electrical signal is then processed and displayed as a measure of heat flux, typically in units of Watts per square meter (W/m^2).
The FHF05 sensor is designed for high accuracy and reliability, making it a popular choice among researchers, engineers, and building professionals. It is also easy to install and can be connected to a data logger or other monitoring system for long-term monitoring and analysis.
A Heat Flux Sensor Example
What Types of Heat Flux Sensors are There?
Heat flux sensors come in various types and designs, each with its own unique features and capabilities. Some of the most common types of heat flux sensors include resistance temperature detectors (RTDs), thermocouples, and thermopiles.
- Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs) are heat flux sensors that use the change in resistance of a material with temperature to measure heat flux. RTDs are highly accurate and have a wide temperature range, making them ideal for use in high-temperature applications such as solar thermal power plants.
- Thermocouples are heat flux sensors that use the difference in voltage between two dissimilar metals to measure heat flux. They are easy to use and are commonly used in building insulation, as well as in solar thermal power plants.
- Thermopiles are heat flux sensors that consist of multiple thermocouples connected in series. They are commonly used in solar radiometers and pyranometers, which are instruments used to measure the amount of solar radiation received by a surface.
What are Calorimeter Heat Flux Sensors?
Calorimeter heat flux sensors measure heat flux using a technique known as the gradient method. They consist of a thermopile, which is a series of thermocouples connected in series or parallel. The thermopile measures the temperature difference across a known thermal resistance, such as a thin layer of insulating material.
The FHF05SC by HuksefluxUSA is a self-calibrating calorimeter heat flux sensor. It combines two sensors in one: a heat flux sensor and a temperature sensor. The temperature sensor allows the FHF05SC to perform self-calibration, ensuring accurate and reliable heat flux measurements. This unique feature makes the FHF05SC ideal for various applications, including HVAC systems and automotive thermal management.
Understanding the Science Behind Heat Flux Sensors
Heat flux sensors are designed to measure the rate of heat flow per unit area. They determine the amount of heat passing through a material, typically a flat surface, in a specific direction. The sensors work by detecting the temperature gradient on the surface, allowing for accurate calculation of the heat flow rate. Heat flux sensors are made from thermoconductors, which are materials that have a high thermal conductivity. This allows for precise temperature measurements, making them ideal for use in high temperature environments.
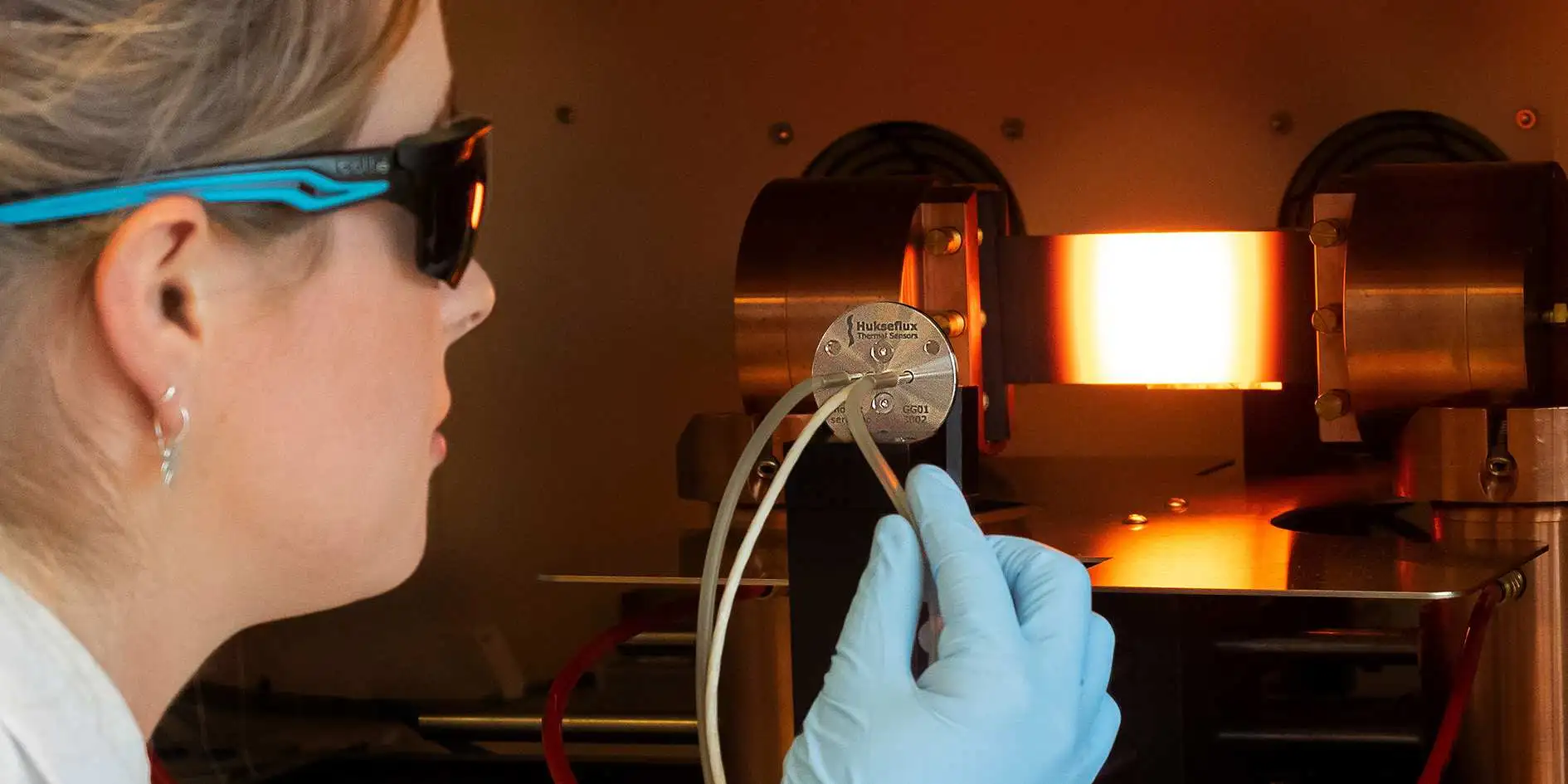

How do Heat Flux Sensors Work and What Makes Them So Effective?
Heat flux sensors work by utilizing the relationship between heat flow, temperature, and material properties. The sensors consist of a thermistor, which is a type of resistor that changes its resistance with temperature, and a metal layer. The metal layer provides good thermal conductivity, allowing for heat to flow freely through the sensor. The thermistor is placed in the middle of the metal layer and is connected to a circuit. As heat flows through the metal layer and into the thermistor, it causes a change in resistance, which can be accurately measured and used to calculate the heat flow rate.
Heat flux sensors are used in a wide range of applications, including:
- HVAC systems: Heat flux sensors are used in HVAC systems to monitor the temperature distribution and heat flow in buildings. They provide critical information for temperature control and energy efficiency, helping to reduce energy costs and improve indoor air quality.
- Automotive industry: In the automotive industry, heat flux sensors are used to monitor the temperature distribution of engine components. They provide valuable information for engine performance and reliability, helping to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions.
- Aerospace industry: Heat flux sensors are used in the aerospace industry to monitor the temperature distribution of aircraft components, such as engines and fuselage. They provide critical information for flight safety and performance optimization.
- Medical industry: Heat flux sensors are used in the medical industry to monitor the temperature distribution in medical devices, such as warming blankets and heating pads. They ensure patient safety by preventing overheating and ensuring accurate temperature control.
Frequently Asked Questions About Heat Flux Sensors
Q: How do heat flux sensors measure heat flow?
A: Heat flux sensors measure heat flow by detecting the temperature gradient on a surface. The sensors consist of a thermistor and a metal layer, which allows for heat to flow freely through the sensor. The change in resistance caused by the flow of heat is measured and used to calculate the heat flow rate.
Q: What are heat flux sensors made of?
A: Heat flux sensors are typically made from thermoconductors, which are materials with high thermal conductivity. This allows for precise temperature measurements and makes them ideal for use in high temperature environments.
Q: What industries use heat flux sensors?
A: Heat flux sensors are used in a wide range of industries, including HVAC, automotive, aerospace, and medical, among others. They provide valuable information for temperature control and process optimization in these industries.
Related Article
Stay up to date with the industry.
